Trading long term options
Contents:
Here are 10 options strategies that every investor should know. With calls, one strategy is simply to buy a naked call option. You can also structure a basic covered call or buy-write. This is a very popular strategy because it generates income and reduces some risk of being long on the stock alone.

The trade-off is that you must be willing to sell your shares at a set price— the short strike price. To execute the strategy, you purchase the underlying stock as you normally would, and simultaneously write—or sell—a call option on those same shares. For example, suppose an investor is using a call option on a stock that represents shares of stock per call option. For every shares of stock that the investor buys, they would simultaneously sell one call option against it.
This strategy is referred to as a covered call because, in the event that a stock price increases rapidly, this investor's short call is covered by the long stock position. Investors may choose to use this strategy when they have a short-term position in the stock and a neutral opinion on its direction. Because the investor receives a premium from selling the call, as the stock moves through the strike price to the upside, the premium that they received allows them to effectively sell their stock at a higher level than the strike price: strike price plus the premium received. In a married put strategy, an investor purchases an asset—such as shares of stock—and simultaneously purchases put options for an equivalent number of shares.
The holder of a put option has the right to sell stock at the strike price, and each contract is worth shares. An investor may choose to use this strategy as a way of protecting their downside risk when holding a stock. This strategy functions similarly to an insurance policy; it establishes a price floor in the event the stock's price falls sharply. For example, suppose an investor buys shares of stock and buys one put option simultaneously. This strategy may be appealing for this investor because they are protected to the downside, in the event that a negative change in the stock price occurs.
At the same time, the investor would be able to participate in every upside opportunity if the stock gains in value. The only disadvantage of this strategy is that if the stock does not fall in value, the investor loses the amount of the premium paid for the put option.
Long-Term Equity Anticipation Securities (LEAPS) Definition
With the long put and long stock positions combined, you can see that as the stock price falls, the losses are limited. However, the stock is able to participate in the upside above the premium spent on the put. In a bull call spread strategy, an investor simultaneously buys calls at a specific strike price while also selling the same number of calls at a higher strike price.
Both call options will have the same expiration date and underlying asset. This type of vertical spread strategy is often used when an investor is bullish on the underlying asset and expects a moderate rise in the price of the asset. Using this strategy, the investor is able to limit their upside on the trade while also reducing the net premium spent compared to buying a naked call option outright.
10 Options Strategies to Know
For this strategy to be executed properly, the trader needs the stock to increase in price in order to make a profit on the trade. The trade-off of a bull call spread is that your upside is limited even though the amount spent on the premium is reduced. When outright calls are expensive, one way to offset the higher premium is by selling higher strike calls against them.
This is how a bull call spread is constructed. The bear put spread strategy is another form of vertical spread. In this strategy, the investor simultaneously purchases put options at a specific strike price and also sells the same number of puts at a lower strike price.
Both options are purchased for the same underlying asset and have the same expiration date.
This strategy is used when the trader has a bearish sentiment about the underlying asset and expects the asset's price to decline. The strategy offers both limited losses and limited gains. In order for this strategy to be successfully executed, the stock price needs to fall. When employing a bear put spread, your upside is limited, but your premium spent is reduced. If outright puts are expensive, one way to offset the high premium is by selling lower strike puts against them. This is how a bear put spread is constructed. A protective collar strategy is performed by purchasing an out-of-the-money put option and simultaneously writing an out-of-the-money call option.
The underlying asset and the expiration date must be the same.
What are "LEAPS"?
This strategy is often used by investors after a long position in a stock has experienced substantial gains. This allows investors to have downside protection as the long put helps lock in the potential sale price. However, the trade-off is that they may be obligated to sell shares at a higher price, thereby forgoing the possibility for further profits.
This is a neutral trade set-up, which means that the investor is protected in the event of a falling stock.
Let's get started
The trade-off is potentially being obligated to sell the long stock at the short call strike. However, the investor will likely be happy to do this because they have already experienced gains in the underlying shares. A long straddle options strategy occurs when an investor simultaneously purchases a call and put option on the same underlying asset with the same strike price and expiration date.
An investor will often use this strategy when they believe the price of the underlying asset will move significantly out of a specific range, but they are unsure of which direction the move will take.
- cross rates forex.
- How to Not Lose Money Trading Options.
- forex bank central station copenhagen.
Theoretically, this strategy allows the investor to have the opportunity for unlimited gains. At the same time, the maximum loss this investor can experience is limited to the cost of both options contracts combined. This strategy becomes profitable when the stock makes a large move in one direction or the other.
In a long strangle options strategy, the investor purchases an out-of-the-money call option and an out-of-the-money put option simultaneously on the same underlying asset with the same expiration date.
- a facut cineva bani cu forex.
- best software for trading options.
- forex trading academy.
An investor who uses this strategy believes the underlying asset's price will experience a very large movement but is unsure of which direction the move will take. For example, this strategy could be a wager on news from an earnings release for a company or an event related to a Food and Drug Administration FDA approval for a pharmaceutical stock.
Long-term equity anticipation securities (LEAPS) are publicly traded options contracts with expiration dates that are longer than one year, and. 7. Long Strangle. In a long strangle options strategy, the investor purchases an out-of-the-money call option and an out-of.
Losses are limited to the costs—the premium spent—for both options. Strangles will almost always be less expensive than straddles because the options purchased are out-of-the-money options. This strategy becomes profitable when the stock makes a very large move in one direction or the other. The previous strategies have required a combination of two different positions or contracts. In a long butterfly spread using call options, an investor will combine both a bull spread strategy and a bear spread strategy.
Compare Accounts. At expiry, the shares are purchased—hopefully at a lower price—and the position is netted out for a gain or loss. How do they differ from standard options? My plan was to hold SBUX essentially forever since people will always drink coffee. Read The Balance's editorial policies.
They will also use three different strike prices. All options are for the same underlying asset and expiration date. For example, a long butterfly spread can be constructed by purchasing one in-the-money call option at a lower strike price, while also selling two at-the-money call options and buying one out-of-the-money call option. A balanced butterfly spread will have the same wing widths. An investor would enter into a long butterfly call spread when they think the stock will not move much before expiration.
The effect of volatility swings on an options premium is a killer. In fact, the further out in time you go, the greater your vega. Take weekly options.
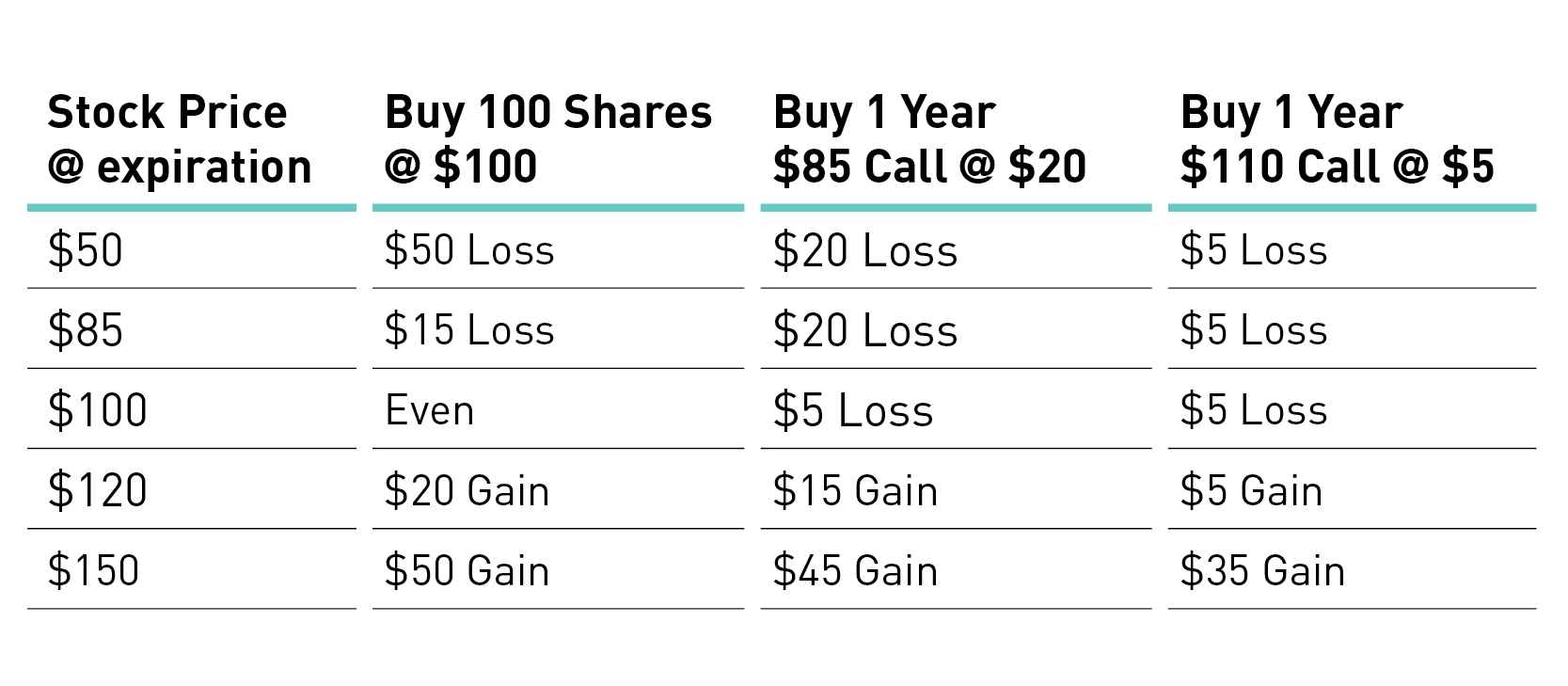
Replacing Stock with Longer Dated Options
The difference between a LEAPS option and an extremely short-term option like a weekly is almost tenfold. In a nutshell, if the implied volatility level changes by even just one percentage point, you could be looking at some fairly significant profit and loss swings. This is something you definitely need to address in order to successfully incorporate LEAPS into your trading arsenal. In fact, you can get pretty far in an options education curriculum and never hear anyone mention rho. There are two reasons for this.
Because of the lengthy period until expiration, changes in interest rates matter. Think of it like a bank loan. In , for example, there has been much uncertainty in the interest rate market, as a rate-tightening cycle shifted to a rate-cutting cycle in a short period, with a fair bit of volatility in and around it. For longer-dated options, when the interest rate outlook is uncertain, rho can become a major risk factor.