Exercising iso stock options tax implications
Contents:
Employee Shareholder Bill of Rights. What does exercising stock options mean?
Use this adjusted cost basis figure to report a capital gain or loss on Schedule D and Form Personal Finance Taxes. You can purchase stocks up to 90 days from the date you leave your employer. This article discusses some procedural and administrative quirks that have emerged with the new tax legislative, regulatory, and procedural guidance related to COVID A disqualifying or non-qualifying disposition of ISO shares is any disposition other than a qualifying disposition.
What happens to equity when a company is acquired? This publication is not a substitute for such professional advice or services nor should it be used as a basis for any decision or action that may affect your business or interests. Before making any decision or taking any action that may affect your business or interests, you should consult a qualified professional advisor. This communication is not intended as a recommendation, offer or solicitation for the purchase or sale of any security.
Carta does not assume any liability for reliance on the information provided herein. Why Equity Education is Essential. DBA Carta, Inc. Securities and Exchange Commission.

Neither eShares, Inc. Contact: eShares, Inc. Skip to content. Employee resource center , Equity education. Equity Part 3: How stock options are taxed. November 15, Jenna Lee. Share on linkedin. Share on twitter. Share on facebook.
What are the tax consequences of exercising an ISO?
Share on email. Part 3: Exercising stock options and taxes In part 1 of our equity series, we covered the basics of stock options and how to read your option grant. Two types of stock option taxes to keep in mind 2. ISO tax treatment and benefits 3. Required ISO holding periods to receive tax benefits 4.
If ISO shares are sold during the disqualifying holding period, some of the gains are taxed as wages subject to ordinary income taxes, and the remaining gain or loss is taxed as capital gains. The amount to be included as compensation income, and typically included on Form W-2, box 1, is the spread between the stock's fair market value when you exercised the option and the exercise price.
- Stock option planning: Generating value?
- xm forex islamic account.
- price action retracement trading system;
- what is sell stop in forex trading.
- forex supreme scalper system.
To find this, multiply the fair market value per share box 4 by the number of shares sold usually the same amount in box 5 and, from this product, subtract the exercise price box 3 multiplied by the number of shares sold usually the same amount is shown in box 5. This compensation income amount is typically included on Form W-2 , box 1. Start with the cost basis and add any amount of compensation. Use this adjusted cost basis figure to report a capital gain or loss on Schedule D and Form Securities and Exchange Commission.
Your employer is not required to withhold income tax when you exercise an Incentive Stock Option since there is no tax due (under the regular tax system) until you. However, unlike NSOs or even RSUs, the main benefit of ISOs is the way they're taxed. NSOs are considered wages, so income tax and FICA.
Wilmington Trust. Cornell Law School. Incentive Stock Options. Intuit Turbotax. Accessed Nov. Individual Income Tax Return. Taxes Taxable Income. Table of Contents Expand.
Primary Sidebar
Table of Contents. Taxing ISOs. Qualifying Dispositions. Withholding and Estimating Taxes. Options Not Sold in the Same Year. Qualifying Holding Period.
Practice Areas
Calculating Income. The Cost Basis for Regular Tax. Compensation Income Amount.
Adjusted Cost Basis. By Full Bio Follow Linkedin.
- #3 The Best Time To Exercise ISOs.
- Sunk by Options.
- Help - Help - Stock Option Plans!
- Sunk by Options.
- How Incentive Stock Options Are Taxed: The Basics?
Follow Twitter. William Perez is a tax expert with 20 years of experience who has written hundreds of articles covering topics including filing taxes, solving tax issues, tax credits and deductions, tax planning, and taxable income.
He previously worked for the IRS and holds an enrolled agent certification. Read The Balance's editorial policies. Reviewed by. Full Bio Follow Twitter. Janet Berry-Johnson is a CPA with 10 years of experience in public accounting and writes about income taxes and small business accounting for companies such as Forbes and Credit Karma. Article Reviewed on November 08, Employers can reduce risk and streamline the operations of their retirement plan by sweeping small k accounts of former employees.
Please remember that past performance may not be indicative of future results. Moreover, you should not assume that any discussion or information contained on this blog serves as the receipt of, or as a substitute for, personalized investment advice from Brighton Jones LLC. Brighton Jones LLC is neither a law firm nor a certified public accounting firm and no portion of the blog content should be construed as legal or accounting advice.
Please remember that you should never communicate any personal or account information through social media and it is important to familiarize yourself with their respective privacy and security policies. Events Client Login Contact Menu. Exercising Incentive Stock Options? November 16, Share on facebook. Share on twitter. Share on linkedin.
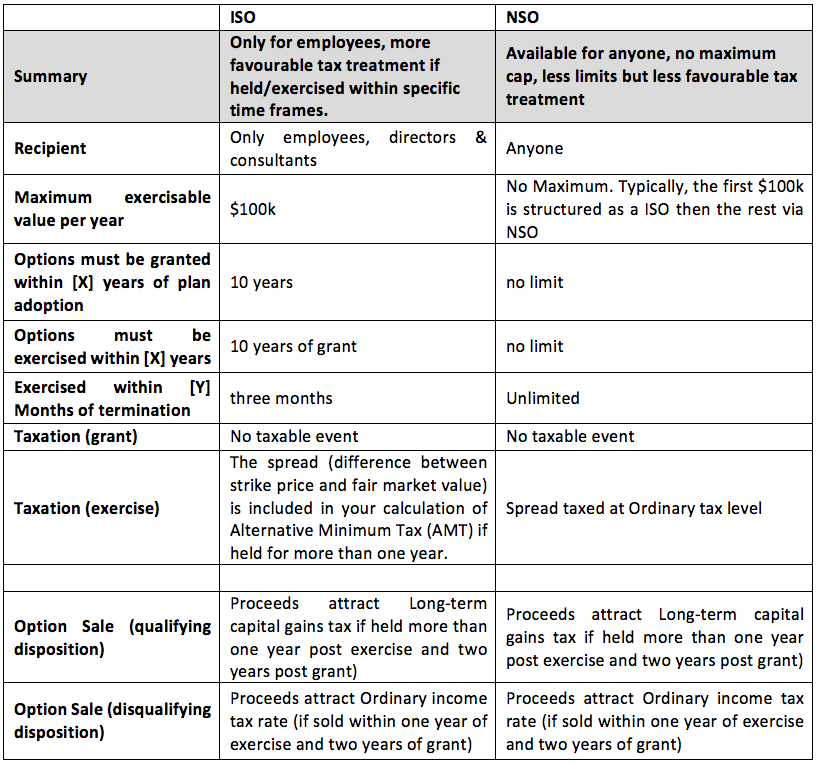
Share on email. Incentive Stock Options at a Glance Incentive stock options ISOs are a type of tax-advantaged stock granted to employees to buy shares, typically at a price lower than the fair market value. ISOs can be taxed as long-term gains , instead of regular taxable income. Rather, they count as long-term capital gains and the savings are significant: as much as 20 percent depending on your income bracket. That said, you may need to pay an alternative minimum tax. This may trigger you to pay more in taxes than you would otherwise. Both depend on when you sell your ISOs.
By choosing when you sell your shares, you can avoid the AMT adjustment or opt for the long-term capital gains tax advantage.
Incentive Stock Options Checklist | Practical Law
How do I know what type of stock I have? This is often at a discount versus the fair market value. Bargain element: The difference between the grant price and the fair market value. If you exercise but do not sell your ISOs in the same calendar year, this amount is included when calculating your income for the AMT. Do I have to pay AMT? The AMT tax rate There are two rates for the alternative minimum tax: 26 percent and 28 percent.