Stock options income taxes
Contents:
If your employer grants you a statutory stock option, you generally don't include any amount in your gross income when you receive or exercise the option. However, you may be subject to alternative minimum tax in the year you exercise an ISO. For more information, refer to the Instructions for Form You have taxable income or deductible loss when you sell the stock you bought by exercising the option.
You generally treat this amount as a capital gain or loss.
However, if you don't meet special holding period requirements, you'll have to treat income from the sale as ordinary income. Add these amounts, which are treated as wages, to the basis of the stock in determining the gain or loss on the stock's disposition. Refer to Publication for specific details on the type of stock option, as well as rules for when income is reported and how income is reported for income tax purposes.
This form will report important dates and values needed to determine the correct amount of capital and ordinary income if applicable to be reported on your return. Employee Stock Purchase Plan - After your first transfer or sale of stock acquired by exercising an option granted under an employee stock purchase plan, you should receive from your employer a Form , Transfer of Stock Acquired Through an Employee Stock Purchase Plan under Section c.
How Stock Options Are Taxed & Reported
This form will report important dates and values needed to determine the correct amount of capital and ordinary income to be reported on your return. If your employer grants you a nonstatutory stock option, the amount of income to include and the time to include it depends on whether the fair market value of the option can be readily determined.
Readily Determined Fair Market Value - If an option is actively traded on an established market, you can readily determine the fair market value of the option. Refer to Publication for other circumstances under which you can readily determine the fair market value of an option and the rules to determine when you should report income for an option with a readily determinable fair market value.
Incentive stock option
If your tentative minimum tax is higher than your regular tax, you may owe the higher of the two. A tentative minimum tax that is the higher of the two is often a direct result of the exercise and hold of ISOs.
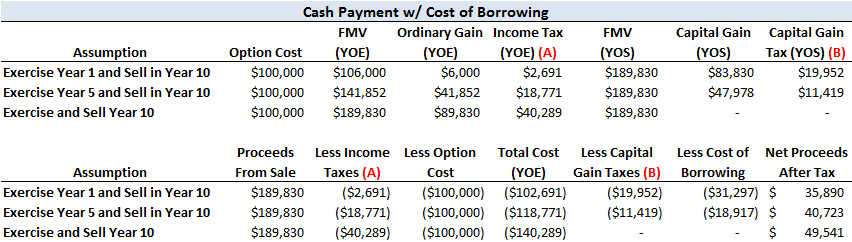
If you are following the above scenario, you may have noticed that you have in fact paid tax twice on a certain portion of the hypothetical example:. Clearly, this would be a disadvantageous tax scenario. Enter the AMT credit.
When you sell your incentive stock option shares in a final sale, you may be able to receive some of the AMT paid back as a credit. This is calculated on your tax return by looking at the difference between regular capital gains and AMT capital gains. This calculation may allow you to receive an AMT credit to cover the tax you already paid.
Said another way, when you sell your shares, you may get some or all of the money you paid on AMT when you exercised and held back to you. This explains why much of the attention surrounding incentive stock options centers around AMT. A significant AMT bill may be a reason or not to exercise your shares.
It should certainly be a reason to consider what your options strategy may be. In addition to AMT, you may want to think about long-term capital gains. When planning for your final sale of stock, it is important to understand what other income you have and how much room you have in various capital gains tax brackets. To do this calculation well, it may take the resources of a good accountant or financial advisor.
Top e-Services
When considering you could pay far less in tax by getting these complicated decisions correct, it may be well worth hiring a professional to help you. You may also need to deal with the net investment income tax NIIT. And while not exactly a direct tax in the same sense as long-term capital gains and net investment income tax, you should still pay attention to how AMT is calculated and how it impacts how much tax you pay. You may face many different types of taxes owed when you have incentive stock options.
The timing of your exercise, hold, and final sale of the stock options can only further intensify the difficulty in understanding which of those taxes apply and what moves to make to reduce your bill. If you find yourself with incentive stock options, begin learning about the tax you may pay and when.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Get_the_Most_Out_of_Employee_Stock_Options_Oct_2020-01-e28cc3504d694dcaaa7a45dfed666f0b.jpg)
If you are not prepared to handle that on your own, it may make sense to work with someone who is an expert in tax and other financial planning needs that can arise. Knowing the rules and planning a good exercise strategy for your incentive stock options can lead to a material difference in the amount you receive in the end.
These company benefits come with taxes that could get a bit complicated.
None of the information in this document should be considered as tax advice. You should consult your tax advisor for information concerning your individual situation. Tax services are not offered through, or supervised by, The Lincoln Investment Companies. The hypothetical examples included are for illustrative purposes only and do not attempt to predict actual results of any particular investment.
Your email address will not be published. Notify me of follow-up comments by email. Notify me of new posts by email. This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed.
Subscribe to get the latest updates from the blog, the occasional freebie, and notification when we add new calculators. Privacy Policy.